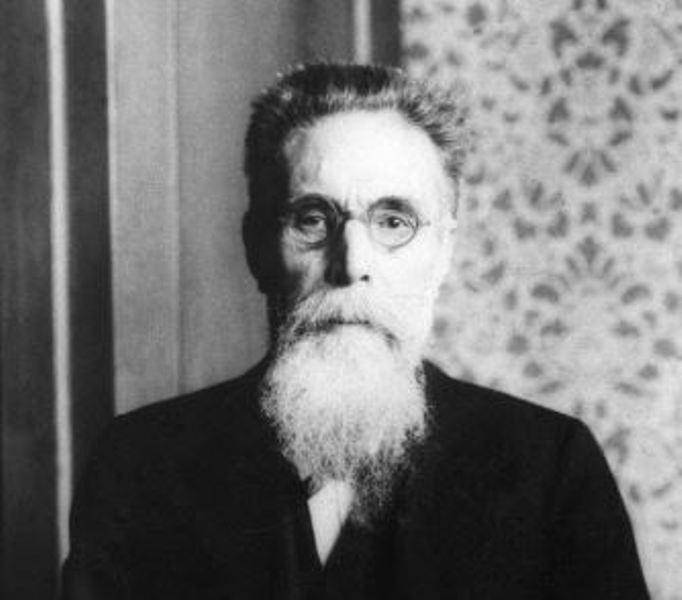
Wilhelm Röntgen Age, Death, Wife, Family, Biography & more
Quick Info→
Age: 77 Years
Wife: Anna Bertha Ludwig
Hometown: Apeldoorn, Holland
| Bio/Wiki | |
|---|---|
| Full name | Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen  |
| Names earned | Father of diagnostic radiology [1]Ramsoft |
| Profession(s) | Physicist, Mechanical Engineer |
| Famous for | • Being the first Nobel Prize winner in physics • Discovering the X-rays |
| Career | |
| Field | Physics |
| Doctoral Advisor | Dr. August Kundt |
| Awards and Honours | • Rumford Medal (1896) • Matteucci Medal (1896) • Elliott Cresson Medal (1897) • Barnard Medal for Meritorious Service to Science (1900) • Nobel Prize for Physics (1901)  • Member of the American Philosophical Society (1897) • Foreign member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (1907) • Honorary Doctor of Medicine from the University of Wurzburg |
| Personal Life | |
| Date of Birth | 27 March 1845 (Thursday) |
| Birthplace | Lennep, now called Remscheid-Lennep, Germany |
| Date of Death | 10 February 1923 |
| Place of Death | Munich, Germany |
| Burial | Roentgen plot in Giessen, Hesse, Germany |
| Age (at the time of death) | 77 Years |
| Death Cause | Carcinoma of the intestine [2]American Journal of Roentgenology |
| Zodiac sign | Aries |
| Signature |  |
| Nationality | • Prussian (1845–1848) • Stateless (1848–1888) • German (1888–1923) |
| Hometown | Apeldoorn, Holland |
| School | • Martinus Herrmann van Doorn, Regentesselman, Netherlands • Utrecht Technical School |
| College/University | • Federal Polytechnic Institute, Zürich (now ETH Zurich) • University of Zurich |
| Educational Qualification(s) | • Mechanical engineering from Federal Polytechnic Institute, Zürich (now ETH Zurich) (1868) • Ph.D. (Philosophy) from University of Zurich (1869)  |
| Religion/Religious Views | Christianity (Protestant) [3]Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen: The Birth of Radiology - Springer Link |
| Hobbies | Hiking, Hunting |
| Relationships & More | |
| Marital Status (at the time of death) | Widower |
| Marriage Date | 19 January 1872 |
| Family | |
| Wife/Spouse | Anna Bertha Ludwig (deceased in 1919)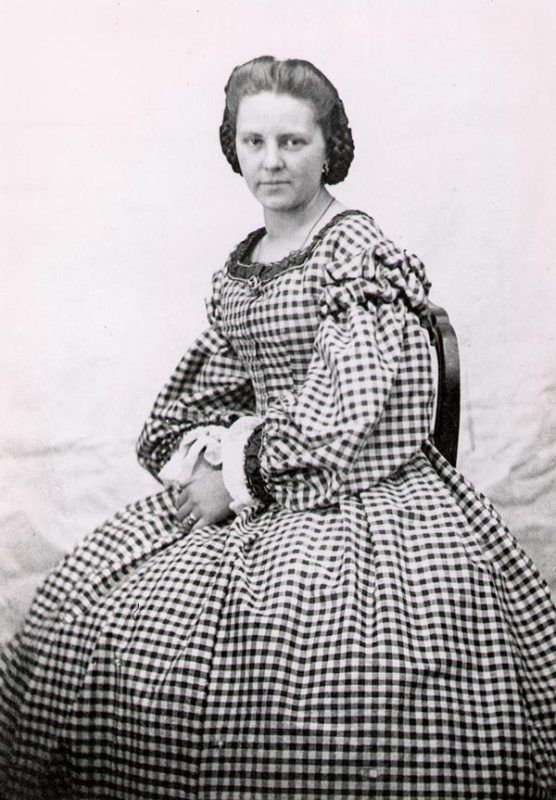 |
| Children | Son- None Daughter- Josephine Bertha Ludwig (adopted)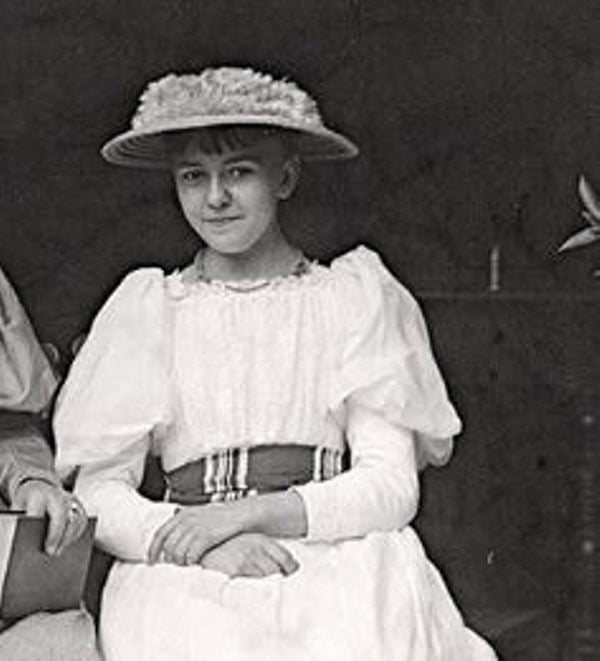  |
| Parents | Father- Friedrich Conrad (1801-1884) (textile merchant) Mother- Constance Charlotte Frowein (1806-1880)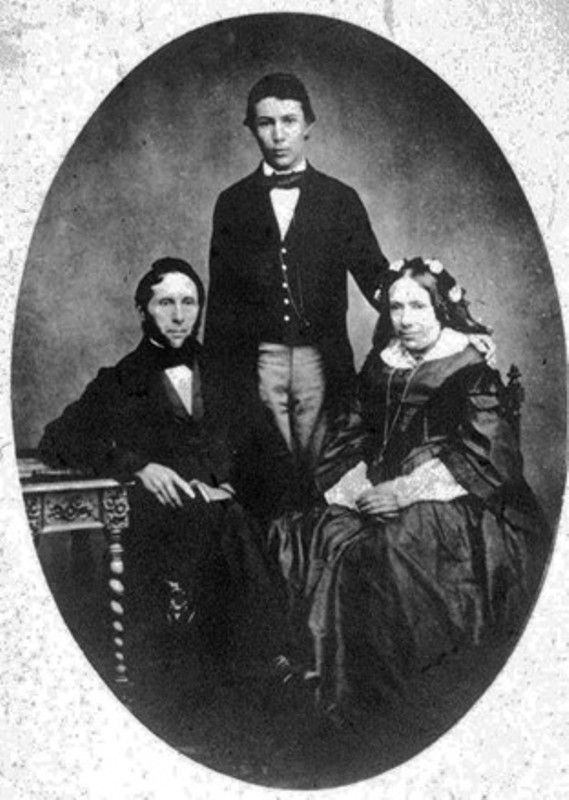  |
| Siblings | Brother- None Sister- None |
| Legacy | |
| Monuments, Buildings, Streets | • A monument of Wilhelm Röntgen by a German architect, Arno Breker, in Lennep (1930)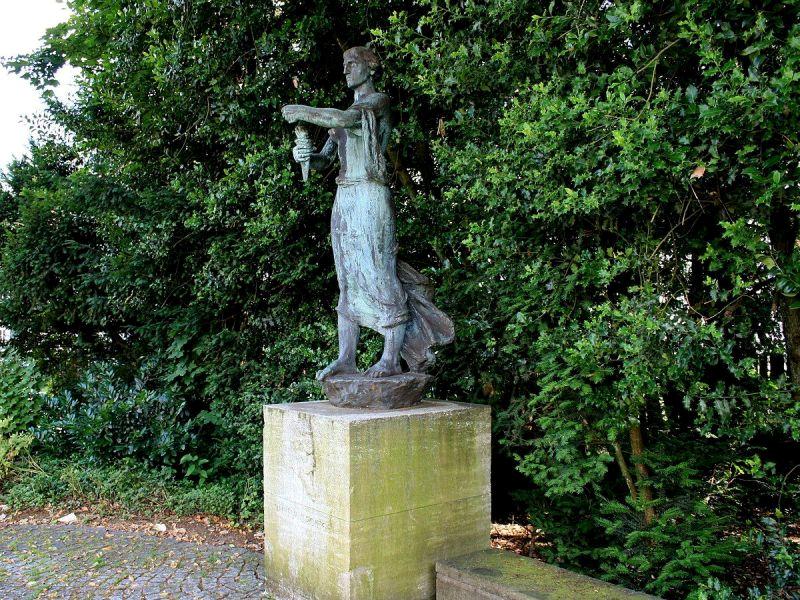 • Deutsches Roentgen Museum in Lennep (1932)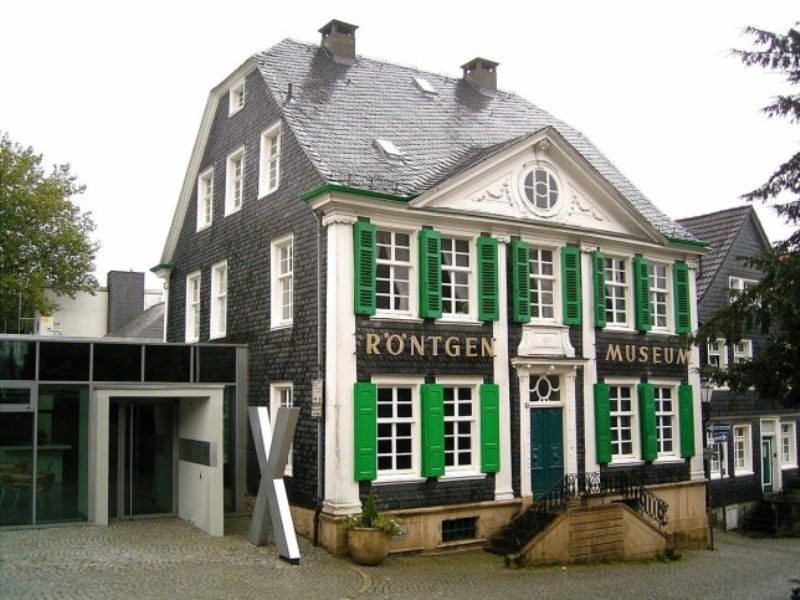  • X-ray monument created by the artist Erich Fritz Reuter in Giessen (1962)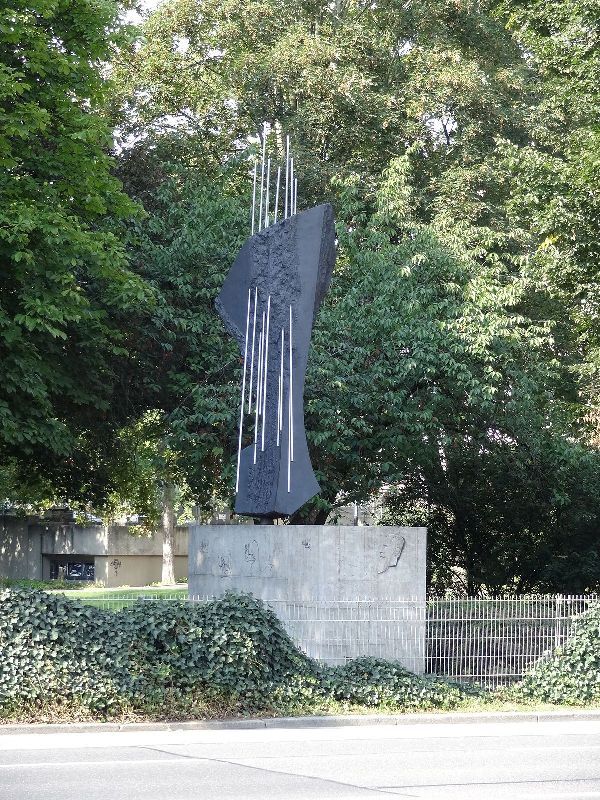  • Röntgen Memorial Site in Würzburg, Germany (1985) • 'Route Röntgen,' a street at CERN, Geneva, Switzerland (2013) Note: Several streets have been named after him in various towns including Apeldoorn in his honour. |
| Places, Things | • Element 111 named as Roentgenium by IUPAC (2004) • A minor planet is named after him as 6401 Röntgen • Röntgen Peak in Antarctica |
Some Lesser Known Facts About Wilhelm Röntgen
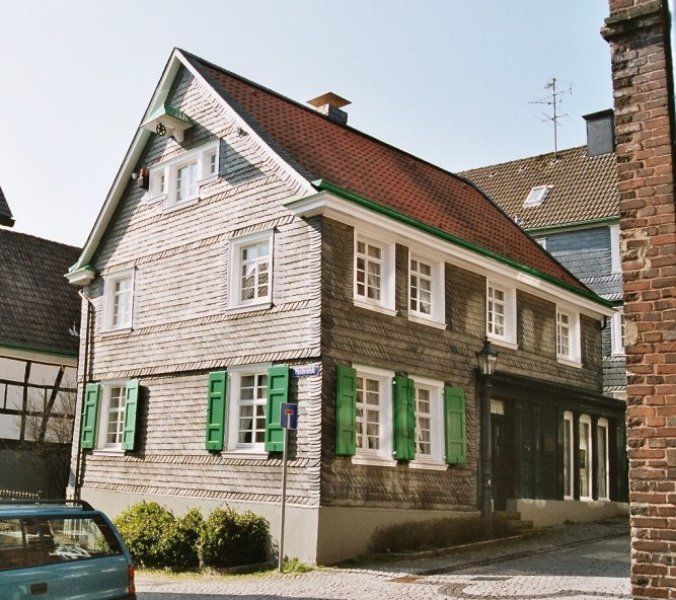
- Wilhelm Röntgen was born in a Burgenland-style home at 287 Poststrasse, Remscheid-Lennep, Germany. He was the only child of his parents, and his mother was a member of an old Lennep family of Dutch heritage.
- Wilhelm Röntgen’s family moved to Apeldoorn, Holland when he was 3 years old because of the civil unrest in Prussia at the time and after shifting to Apeldoorn they lost their Prussian citizenship and became Dutch Citizens.
- He was a member of the Dutch Reformed Church.
- After moving to Utrecht for school, he stayed at Dr Jan Willem Gunning’s house, a well-known Chemist in Utrecht.
- He was expelled from the Utrecht Technical School in 1863 because he was accused of creating a caricature of his professor, which was supposedly drawn by some other student.
- He worked at the University of Utrecht for a while, auditing some courses.
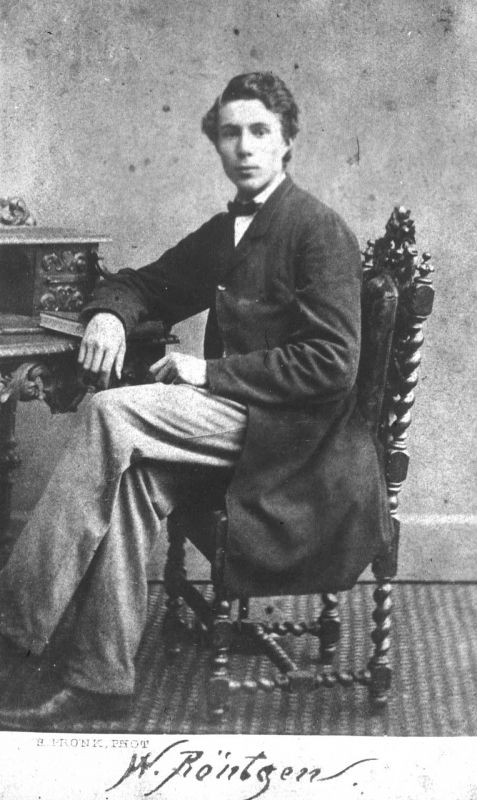
- After hearing that they did not require a technical school diploma for admission to the Mechanical Technical Division of the Zurich Polytechnical School, he applied and got accepted. He moved to Zurich on 16 November 1865.
- After graduating from Zurich Polytechnical School (now ETH Zurich), he attended lectures by Dr August Kundt and Rudolf Clausius at the University of Zurich.
- He proposed to Anna Bertha Ludwig, the daughter of Ludwig who owned a local inn named ‘Zum Grunen Glas,’ on the day he received his degree in mechanical engineering in 1868.
- Before their marriage, Anna Bertha went to Apeldoorn to learn German cooking and housekeeping from Wilhelm Röntgen’s family.
- He worked as an assistant to Professor August Kundt at Julius Maximilians University of Wurzburg, Germany in 1870.
- Two years later, he joined August Kundt at the Kaiser Wilhelm University of Strasbourg under German rule (at the time) to work as his assistant.
- Wilhelm Röntgen got married to Anna Bertha Ludwig on 19 January 1872 at his old Roentgen home in Apeldoorn.
- He passed the exams for privatdozent at the University of Strasbourg on 13 March 1874.
- At the age of 30, he was offered a full professorship in physics and mathematics at the Academy of Agriculture in Hohenheim in Württemberg. He accepted the offer as it came with benefits like German citizenship, a higher salary, and a civil service status.
- He was called for the chair for theoretical physics at the Kaiser Wilhelm University of Strasbourg in 1876, which he accepted.
- He left Strasbourg to assume a full professorship at Justus von Liebig University of Giessen on 1 April 1879.
- After a year in Giessen, he was offered the position of professor of physics and director of the Physical Institute at the University of Wurzburg.
- The couple had no children but adopted Josephine Bertha Ludwig (then aged six) after the death of Josephine’s father, Hans Ludwig, in 1887. Hans Ludwig was the only brother of Anna Bertha.
- Wilhelm Röntgen and his wife returned to Wurzburg on 1 October 1888. He produced seventeen important papers during his time at Wurzburg.
- He was elected as the president of the Julius Maximilian University in Wurzburg for two consecutive years (1894 and 1895).
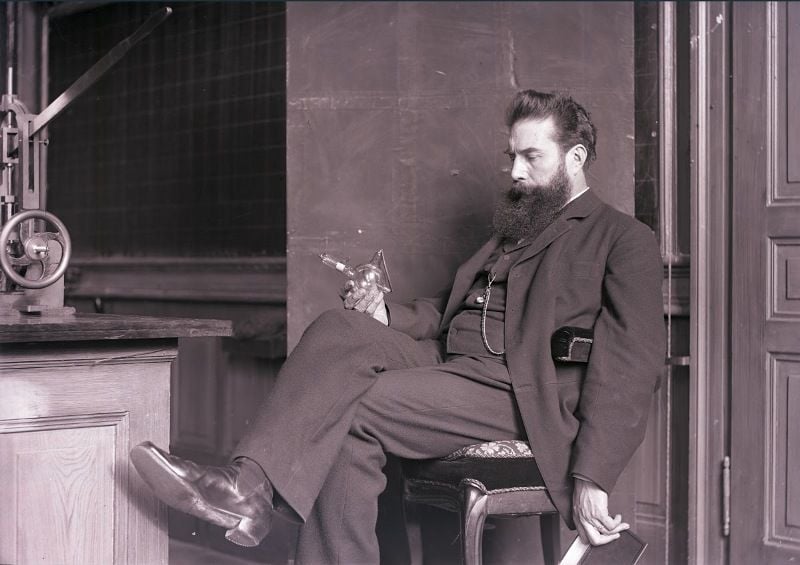
- Wilhelm Röntgen started his experimental work on Cathode rays in October 1895.
- He assembled the apparatus for the experiments by using a large Ruhmkorff induction coil, Deprez interrupter, Hittorf-Crookes tubes, Lenard tubes, and a Raps vacuum pump.
- While conducting the experiments, he discovered that if the discharge tube was encased in cardboard connected to a Ruhmkorff coil, and if he worked in a dark room, a continued fluorescence of a faint green cloud of flickering light waves moving in unison was visible on a small piece of paper painted with barium platinocyanide on 8 November 1895.
- His findings led to the discovery of a new type of highly penetrating ray known as X-rays. He examined all kinds of objects such as a set of weights, a coil of wire, a compass, the barrel of his shotgun, different types of wood and paper, and glass.
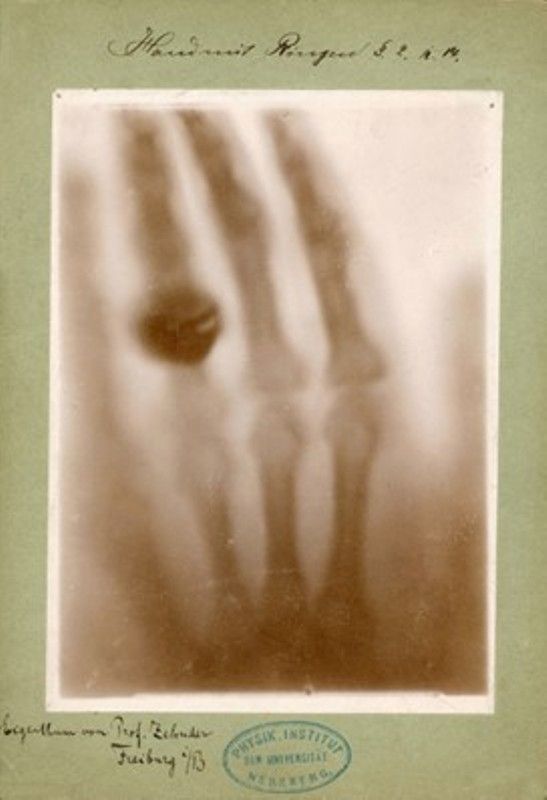
- The first human X-ray was recorded on 27 December 1895, which Wilhelm Röntgen performed on his wife’s hand. Amazed after witnessing this discovery, Anna Bertha said,
I have seen my death.”
- Röntgen completed his research and major observations by the end of December and delivered his historic paper titled ‘On the new kind of rays’ to the Wurzburg Physical Medical Society on 28 December 1895.
- He presented his work to Emperor Wilhelm II in Berlin on 13 January 1896. This was the first and only time he presented his work.
- He was offered the position of chair of physics and director of the Physical Science Institute at the Ludwig Maximilians University of Munich by the Bavarian government, which he accepted. He moved to Munich on 23 March 1900 and stayed there for the remainder of his life.
- During his time in Munich, he enjoyed hunting and had a hunting lodge south of Munich in Weilheim, where he spent a lot of time with his friends.
- The German Roentgen Society placed a plaque on the Roentgen home on 27 March 1920. It translates, “In this house, the discoverer of the rays that were named for him,
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, was born on 27 March 1845. His home town declared him an honorary citizen in 1896.”
- Wilhelm Röntgen never registered a patent for his discovery for ethical reasons as he wanted the world to benefit from it.
- In 1922, a plaque was placed on the house where he lived until 1869 in Zurich to commemorate him. It translates,
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, the discoverer of the rays named after him, lived here from 1866 to 1869 as a student at the Federal Technical High School.”
- Wilhelm Röntgen, in his will, declared that the equipment he used during his rays discovery should be given to the famous Deutsches Museum in Munich.
- He donated the Nobel Prize money (50,000 Swedish crowns) to the University of Würzburg, which awarded him with an honorary Doctor of Medicine.
References/Sources: